In a world dominated by electronics and connected objects, battery-free watches represent an island of watchmaking tradition that continues to fascinate enthusiasts and collectors. These mechanical masterpieces are a testament to centuries-old expertise that combines technical precision and aesthetic beauty. But how exactly do these timepieces work, defying time without ever needing a battery? Let's dive into the fascinating world of mechanical watchmaking.
The different types of battery-free watches
Unlike quartz watches, which draw their power from a battery, battery-free watches operate using purely mechanical energy. There are two main categories:
Hand-wound mechanical watches
These watches, direct descendants of the first pocket timepieces, require regular winding by their owners. The daily winding action, usually performed by turning the crown, tightens the barrel spring, which stores the energy needed to keep the watch running for the next 24 to 48 hours, depending on the model.
Automatic mechanical watches
An ingenious evolution of manual watches, automatic models incorporate a system that uses the natural movements of the wrist to wind the mechanism. An oscillating weight pivots inside the watch and transmits kinetic energy to the barrel spring. For an active wearer, the watch thus continuously winds itself without manual intervention.
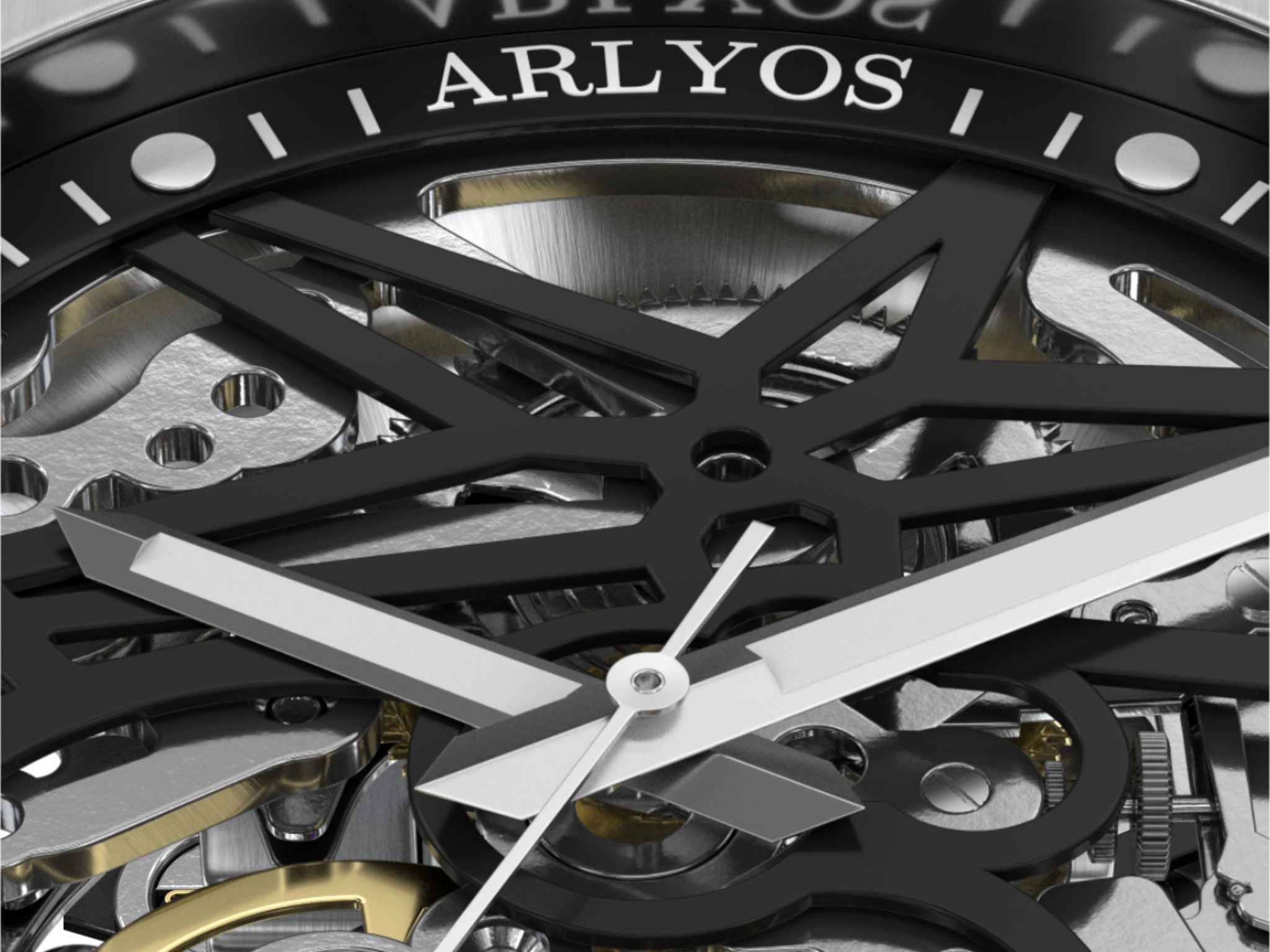
Skeleton watches: when mechanics become art
Among automatic watches, automatic skeleton watches occupy a special place. These timepieces are distinguished by their openwork dial and movement, revealing the usually hidden inner workings and mechanisms. The complex architecture of the bridges and plates is expertly hollowed out to reveal the beauty of the moving gears, creating a true kinetic sculpture on the wrist. Mechanical watch enthusiasts can thus constantly admire the synchronized dance of the components as they mark the passage of time.
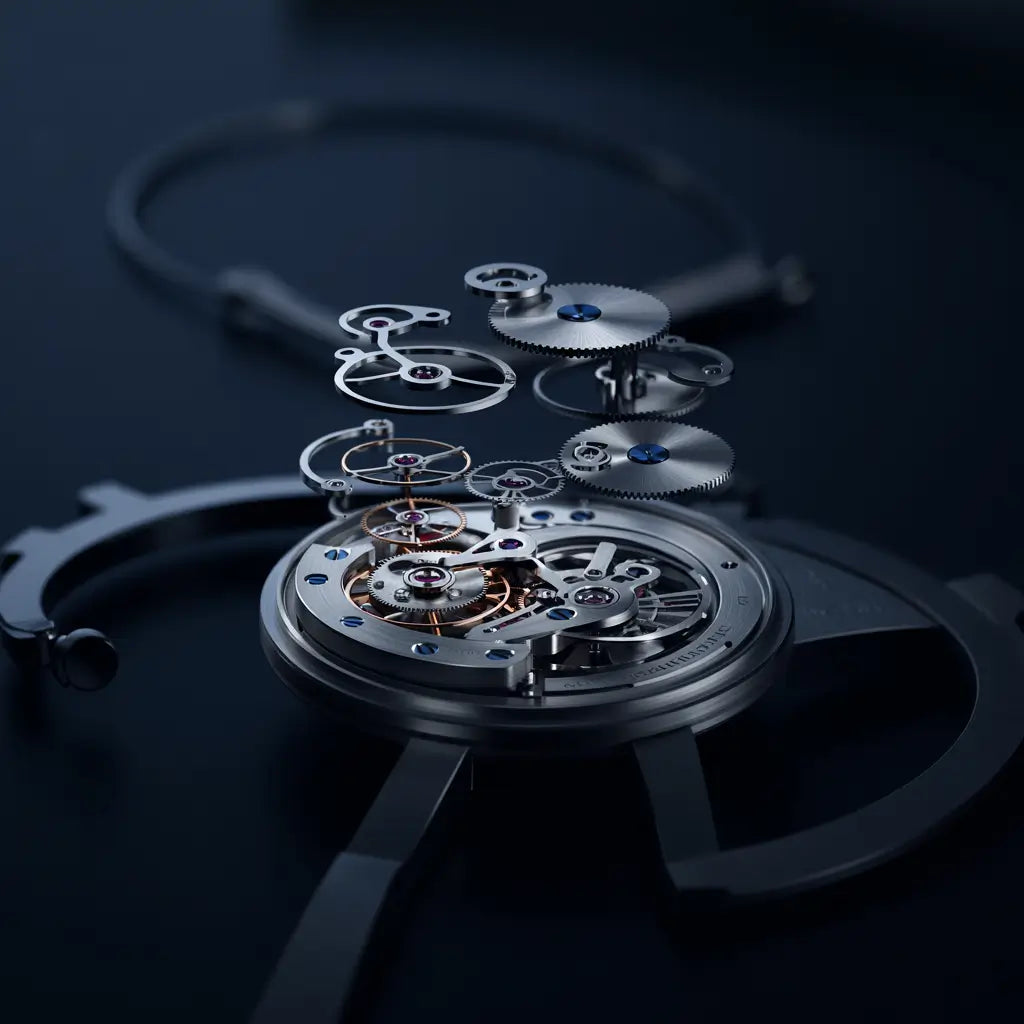
Anatomy and operation of a mechanical watch
To understand how a battery-free watch works, it is essential to know its main components and how they interact.
The essential components
A mechanical watch is made up of several key elements:
-
The barrel and its spring : the watch's true energy reservoir, the barrel spring stores the mechanical force which will be released gradually.
-
The cog : set of gears that transmits energy from the barrel to the hands and escapement.
-
Escapement : A mechanism that transforms the continuous rotation of the gear train into rhythmic pulses. The anchor escapement is the most commonly used in modern watchmaking.
-
The balance spring : regulating organ which beats at a constant frequency (generally between 21,600 and 28,800 vibrations per hour) and gives the watch its precision.
-
The dial and hands : visual interface for reading the time.
The energy cycle
When you wind a mechanical watch, you tension the barrel spring, storing potential energy. This energy is then released in a controlled manner through the gear train to the escapement, which, in conjunction with the sprung balance, distributes this energy in regular pulses. These pulses advance the hands at a precise rate, marking the passage of time.
The power reserve
The length of time a mechanical watch can run without being wound is called its "power reserve." It typically ranges from 40 to 80 hours depending on the model, with some high-end watches able to achieve up to 10 days of power reserve thanks to multiple barrels or more efficient springs.
The specificities of automatic watches
Automatic watches operate on the same principles as manual mechanical watches, but incorporate an ingenious self-winding system.
The oscillating weight winding system
The heart of the automatic system is the oscillating weight (or rotor), a semicircular part generally made of heavy metal that pivots freely around its central axis. When the wearer moves their wrist, the weight rotates, activating a mechanism that transmits this movement to the barrel spring, gradually tensioning it.
Most automatic systems are bidirectional, meaning the weight winds the spring regardless of its direction of rotation. Limiting mechanisms prevent overwinding, which could damage the spring.
Advantages over manual watches
Automatic watches have several advantages:
- Ease of use : no need for daily winding
- Optimal precision : constant winding maintains ideal spring tension
- Watertightness preserved : less handling of the crown reduces the risk of water infiltration
However, after several days without being worn, an automatic watch will stop when its power reserve is exhausted. It will then require gentle manual winding or movement to restart it.
How to identify a watch without a battery
There are several characteristics that allow you to recognize a mechanical or automatic watch:
Distinctive visual signs
-
The movement of the second hand : unlike quartz watches whose second hand advances in jerks (one second at a time), that of a mechanical watch performs a continuous and fluid movement.
-
Transparent case back : Many mechanical watches feature a transparent sapphire crystal case back allowing you to admire the movement.
-
Case thickness : Generally, mechanical watches are thicker than quartz watches due to the complexity of their mechanism.
Testing the second hand movement
Pay close attention to the movement of the second hand: if it moves smoothly and continuously, it's probably a mechanical watch. If it moves in sharp, one-second increments, it's a quartz watch.
Observation of the case back
If the watch case is transparent, you can directly observe the movement. In automatic watches, you will see the oscillating weight move when you move the watch. Manual mechanical watches will have a movement without an oscillating weight, while quartz watches will have an electronic circuit and a battery.
The advantages of mechanical watches
Battery-free watches have many advantages that explain their continued appeal despite the advent of digital technologies.
Durability and longevity
A well-maintained mechanical watch can last for generations. Unlike electronic watches, which often become obsolete, mechanical watches benefit from a timeless design and parts that can be replaced by skilled watchmakers.
Heritage value
Quality mechanical watches often retain their value over time, with some even becoming profitable investments. They can be passed down as family heirlooms, carrying with them a special story and emotion.
Energy independence
The absence of a battery eliminates the worry of replacing batteries and ensures that your watch will never stop unexpectedly due to lack of power (as long as it is worn regularly or manually wound).
Maintenance of watches without batteries
To ensure the longevity and precision of your mechanical watch, regular maintenance is necessary.
Frequency of revisions
It is generally recommended to have a mechanical watch serviced every 3 to 5 years by a qualified watchmaker. This service includes completely disassembling the movement, cleaning all parts, lubricating friction points, and adjusting the accuracy.
Recommended daily practices
- Regular winding : For manual watches, adopt a daily winding routine, ideally at the same time.
- Avoid over-winding : stop as soon as you feel resistance while winding.
- Setting the date : Avoid setting the date between 9 p.m. and 3 a.m., when the date change mechanism is engaged.
Precautions for use
- Shocks and vibrations : Avoid wearing your mechanical watch during intense sporting activities or heavy manual work.
- Magnetic fields : Keep your watch away from strong magnetic fields (magnets, certain electronic devices) which can affect its accuracy.
- Water resistance : Have your watch's water resistance checked regularly, particularly before exposing it to water.
Watch complications
Beyond simply telling the time, mechanical watches can incorporate various additional features called "complications."
Definition and types of complications
A watch complication is any function of a mechanical watch other than simply displaying hours, minutes, and seconds. Each complication adds dozens, or even hundreds, of additional components to the movement.
Examples of common complications
- Calendar : simple (date), complete (day, date, month) or perpetual (automatic adjustment including leap years)
- Chronograph : function for measuring time intervals
- Moon phase : display of lunar cycles
- GMT/Second time zone : simultaneous indication of two different time zones
- Tourbillon : rotating device compensating for the effects of gravity on accuracy
- Minute repeater : audible mechanism indicating the time on demand
These complications not only increase the technical and financial value of a watch, but also its appeal to collectors.
Buying guide: choosing your watch without a battery
Purchasing a mechanical watch often represents a significant investment. Here are some criteria to guide your choice.
Selection criteria
- The movement : origin (Swiss, Japanese, French, etc.), finishes, number of jewels and power reserve.
- Materials : stainless steel, titanium, gold or other precious metals for the case; sapphire, mineral or plexiglass crystal for the dial.
- Style : sporty, classic, vintage or contemporary depending on your personal preferences and occasions of use.
- Complications : Choose based on your actual needs and budget.
- Waterproofness : from 30m (splash resistance) to 300m+ for professional diving.
Conclusion
Battery-free watches represent much more than simple timekeeping instruments. They embody centuries-old watchmaking heritage, craftsmanship, and sustainable design that contrasts with our contemporary consumer society.
Choosing a mechanical or automatic watch means choosing an object that can accompany you throughout your life and be passed down to future generations. It also means choosing authentic watchmaking art, where each component is precisely crafted and assembled to create a harmonious whole that defies time.
Whether you are attracted by the aesthetics of visible movements, mechanical precision or heritage value, a battery-free watch will offer you a unique watchmaking experience, far from the ephemeral electronic gadgets of our time.
Did this article help you better understand how battery-free watches work? Feel free to share your questions or experiences with these mechanical timepieces in the comments below.
Read more

When purchasing an automatic skeleton watch, every detail counts, including the type of clasp you choose for your strap. There are two main options available to you: the pin buckle and the folding ...

Explore our comprehensive watch terminology guide with over 100 technical terms explained: movements, complications, materials, and finishes. Essential reference for watch enthusiasts.



Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.